Module II – Monitoring the metrics that matter
On the road to fleet health, let key metrics be your map for keeping your vehicles performing optimally. What metrics matter most to your fleet?
Maintaining the health of your vehicle fleet is crucial for efficient operations and safety. This module will guide you through essential metrics to monitor during inspections, providing detailed checklists to make sure nothing is overlooked. By following these guidelines, you'll be able to keep your fleet in top condition and better avoid costly repairs.
What are fleet health metrics?
Fleet health metrics are quantifiable measures that help assess and improve your fleet vehicles' overall condition and performance, such as fluid levels, tire performance, brake function and engine diagnostics. They provide valuable insights into the vehicles' mechanical health, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
By tracking and analyzing these metrics, you can identify potential issues before they become serious problems, implement targeted maintenance strategies and maintain your fleet's safe and efficient operation. This approach not only reduces operational costs and minimizes downtime but also helps extend vehicles' lifespans, ultimately enhancing your fleet's productivity and reliability..
Did you know?
Maintenance costs typically make up 30% to 50% of the total cost of ownership for fleets.
What are the key metrics to continuously monitor for fleet health?
Monitoring key metrics during vehicle inspections is essential for maintaining fleet health, as it helps identify potential issues before they escalate into larger, costlier repairs. Fleet managers can significantly enhance vehicle safety, maximize efficiency and achieve reliability by prioritizing checks around fluid levels, tire performance, brake function and engine performance. This proactive approach leads to reduced operational costs, minimized downtime and increased fleet longevity.
Fluid levels
How: Monitor the fluid levels for engine oil, coolant and vehicle fluids like brake fluid, power steering fluid, window washing fluid, transmission fluid, etc.
Why: Without these fluids, increased friction, overheating and component wear and tear can occur, leading to more frequent breakdowns and higher maintenance costs. These issues can ultimately affect the reliability and safety of the entire fleet.
Tire performance
How: Verify that tire pressure readings are at recommended levels and conduct regular inspections for signs of wear and damage, such as tread depth and sidewall cracks. In addition, balance tires and align vehicles’ steering periodically.
Why: Proper tire maintenance can help prevent collisions, improve fuel efficiency and extend your tires' lifespans.
Brake function
How: Regularly inspect brake components, such as pads, rotors, calipers and brake lines, for signs of wear and tear, leaks, or damage. Check brake fluid levels and their colors.
Why: Proper brake maintenance will help to keep the hydraulic system operating effectively, enabling reliable vehicle stopping power. Taking care of your vehicles’ brakes helps prevent collisions and can extend the life of your braking systems’ various components. Discolored fluid can indicate leaks or contamination.
Engine performance
Why: Proper engine maintenance helps promote reliable operation, improves fuel efficiency and can prevent costlier repairs, enhancing your fleet's overall performance and safety. The following are examples of components to measure and monitor, including a brief explanation of why each is vital to your fleet’s health.
Air and fuel filters
Why: Maintaining these components is vital for engine performance. Air filters prevent dust, dirt and other airborne particles from entering the engine's combustion chamber, which can cause wear and tear on internal components. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, leading to reduced power output and poor fuel economy. Fuel filters remove contaminants like dirt, rust and debris from the fuel before it reaches the engine. This promotes smooth fuel flow and prevents clogging which can lead to issues like engine misfires, stalling or difficulty starting the vehicle.
Engine oil levels
Why: Low oil levels can lead to increased friction, overheating or a buildup of contaminants, which can compromise the combustion chamber seal. This can cause damage that results in reduced vehicle performance, lifespan and even potentially engine failure.
Engine diagnostic checks
How: An engine diagnostic check involves accessing and analyzing data from the engine's computer to identify potential issues and assess its overall health. This can be done by using a OBD-II diagnostic scanner or an advanced telematics device to retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), display live data and interpret the results.
Why: This check helps identify potential issues early on, helping to prevent costlier repairs and maintain optimal engine operation. By analyzing engine data, diagnostic checks can reveal problems like sensor malfunctions, emissions issues and performance degradation. Addressing these issues proactively can improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions and extend the lifespan of the engine.
Engine performance metrics
How: The key methods to effectively monitor engine performance, such as fuel consumption, power output and emissions - involves leveraging an advanced telematics solution to collect and analyze vehicle data and identify trends.
Why: By tracking metrics like fuel consumption, engine load and emissions, you can identify potential issues early on and save more money. This data can also be used to optimize driving behavior, reduce fuel consumption and minimize environmental impact. To learn more about saving money in your fleet operations, we encourage you to check out our other learning path: The Road to Lower Costs.
Setting benchmarks and targets is also essential for evaluating your fleet's performance and planning future goals. Historical data serves as a baseline, fostering realistic target-setting.
Cooling system
Including the radiator, water pump and coolant levels.
How: To keep your vehicles’ cooling systems running optimally:
- Check the coolant level in the reservoir tank and inspect for any signs of coolant leaks
- Examine hoses for cracks, bulges or signs of wear
- Check the condition and tension of belts connected to the water pump and cooling fan
- Check the pressure while keeping an eye on the temperature gauge
- Lastly, check for contamination, rust or a burnt smell
Why: Maintaining your cooling systems can help prevent engine overheating, coolant leaks and possible engine failure.
Ignition components
How: Regularly inspect the following:
- Spark plugs and spark plug wires
- Ignition coils, ignition switch and ignition control module (ICM)
- Distributor, battery and crankshaft position sensor
Why: Well-maintained ignition components promote engine reliability, performance and efficiency. Faulty ignition components, such as worn-out spark plugs, damaged ignition coils or failing sensors, can lead to misfires, reduced power, increased fuel consumption and even engine damage.
Problems with ignition components can arise by not monitoring and maintaining these parts.
Preventive Maintenance Compliance (PMC)
How: PMC = # of PM tasks completed on time ÷ total # of scheduled PM tasks × 100
To illustrate with an example: If a fleet had 100 scheduled preventive maintenance tasks for a month, and 90 of these were completed on time, the PMC would be: 90%
PMC = (90 ÷100) × 100 = 90%
Why: PMC can be used as a benchmark on how well a fleet is adhering to its preventative maintenance schedule. In the illustration above, the 90% PMC indicates that the fleet is completing most of its scheduled maintenance tasks on time, but there's still room for improvement. It's important to note that while this basic formula is widely used, some organizations may adapt it or use additional metrics to get a more comprehensive view of their maintenance compliance.
Did you know?
Tires, tubes, liners and valves often make up 43% of total maintenance and repair costs for fleets.
Your go-to fleet maintenance checklist
Using the right inspection checklist can effectively address fleet maintenance challenges. A well-organized maintenance program combines routine inspections, fluid checks and component replacements. Sticking to a consistent checklist can prevent costly breakdowns and help maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Use the following checklist to make sure you don't overlook essential routine inspections.
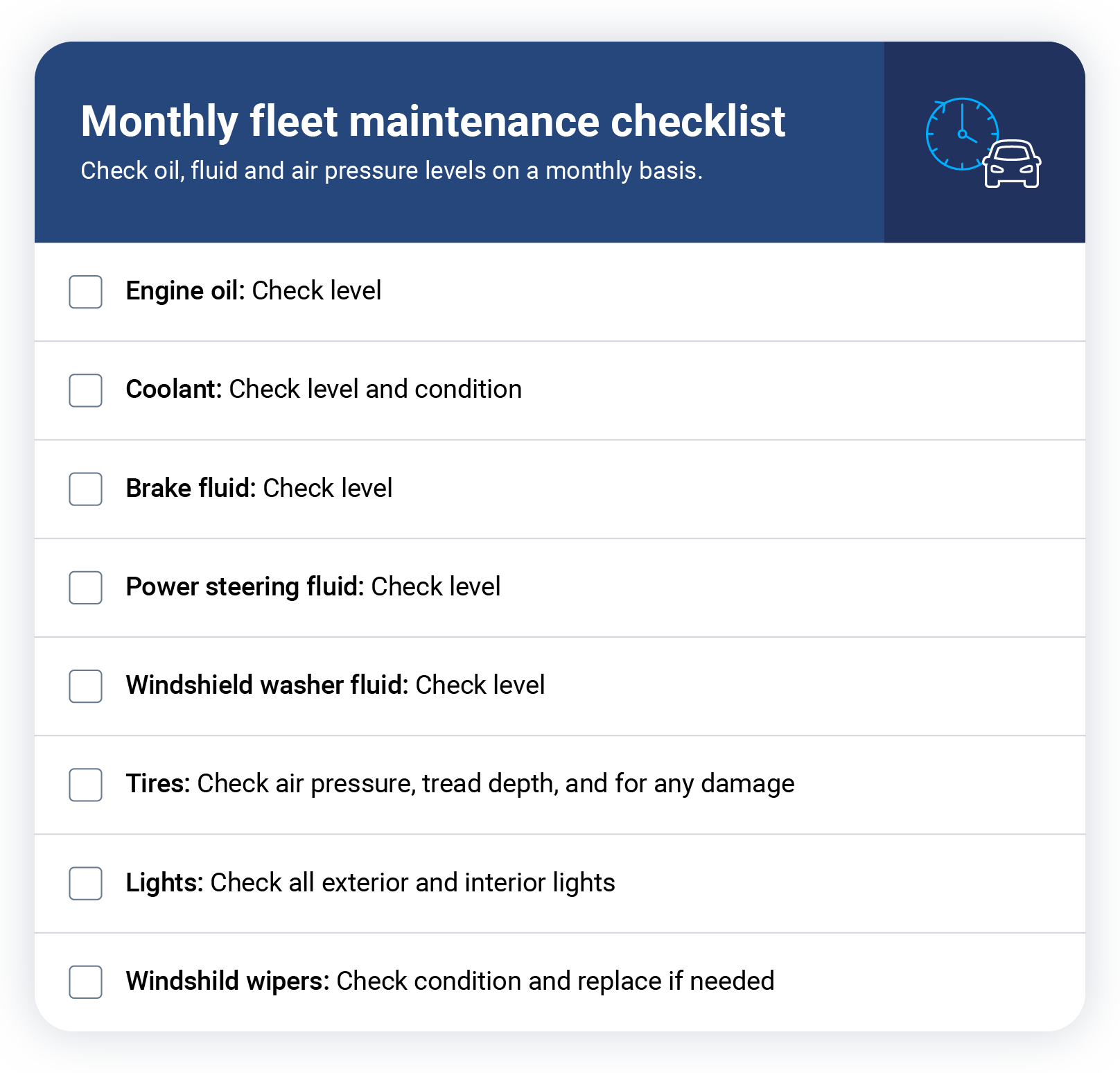
Monthly maintenance checklist
Monthly maintenance checks are essential for keeping your fleet vehicles running smoothly daily. Ignoring things like low oil and fluid levels can damage key parts of the vehicle and cause safety problems later on.
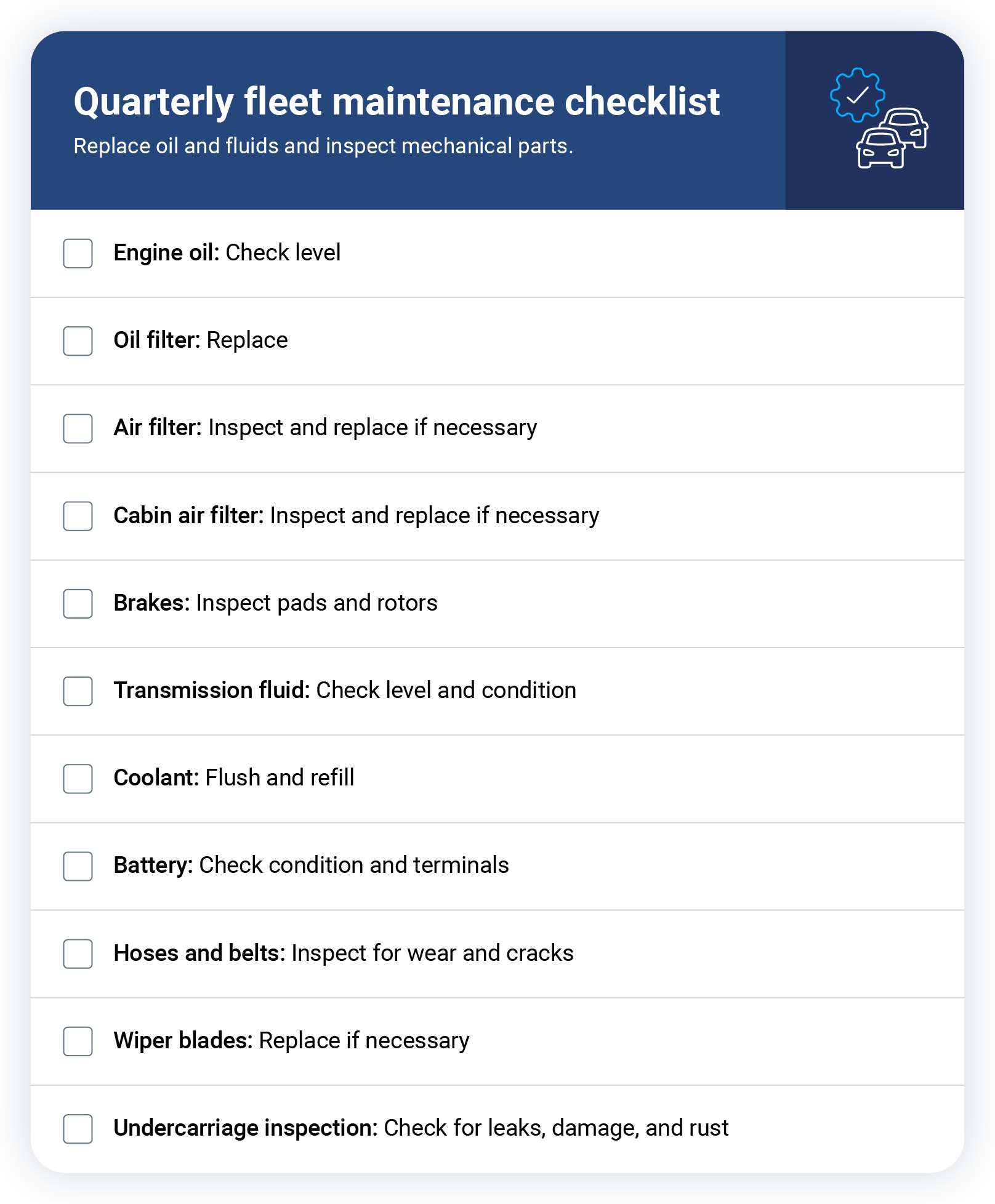
Quarterly maintenance checklist
Just like monthly maintenance, quarterly checks help prevent vehicle downtime. In addition to regular oil, filter and fluid checks, it's essential to make sure your vehicles’ brakes and batteries are working well.
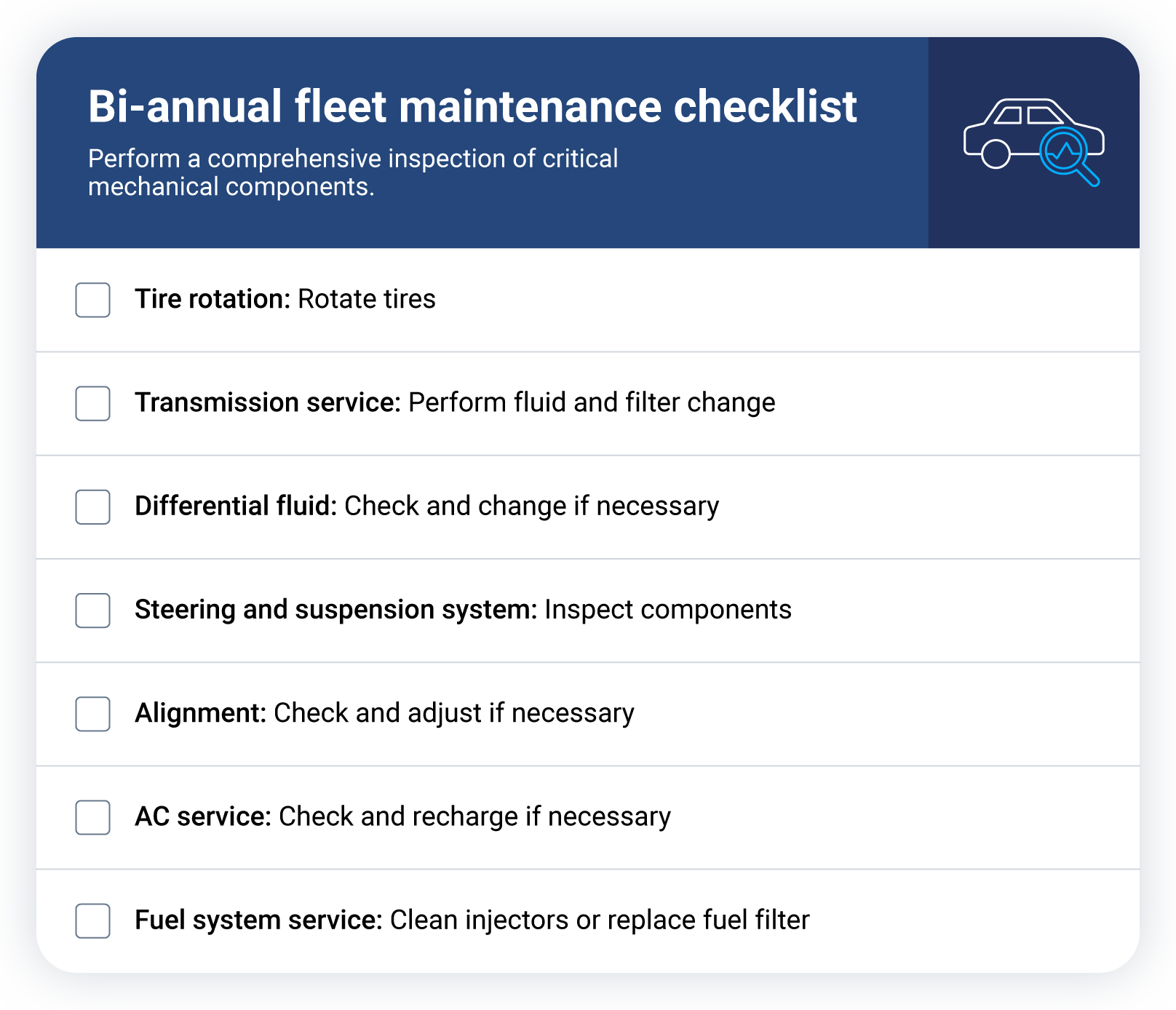
Bi-annual maintenance checklist
Bi-annual maintenance involves more detailed inspections, including checking for leaks, changing filters and replacing parts to keep your fleet running at its best.
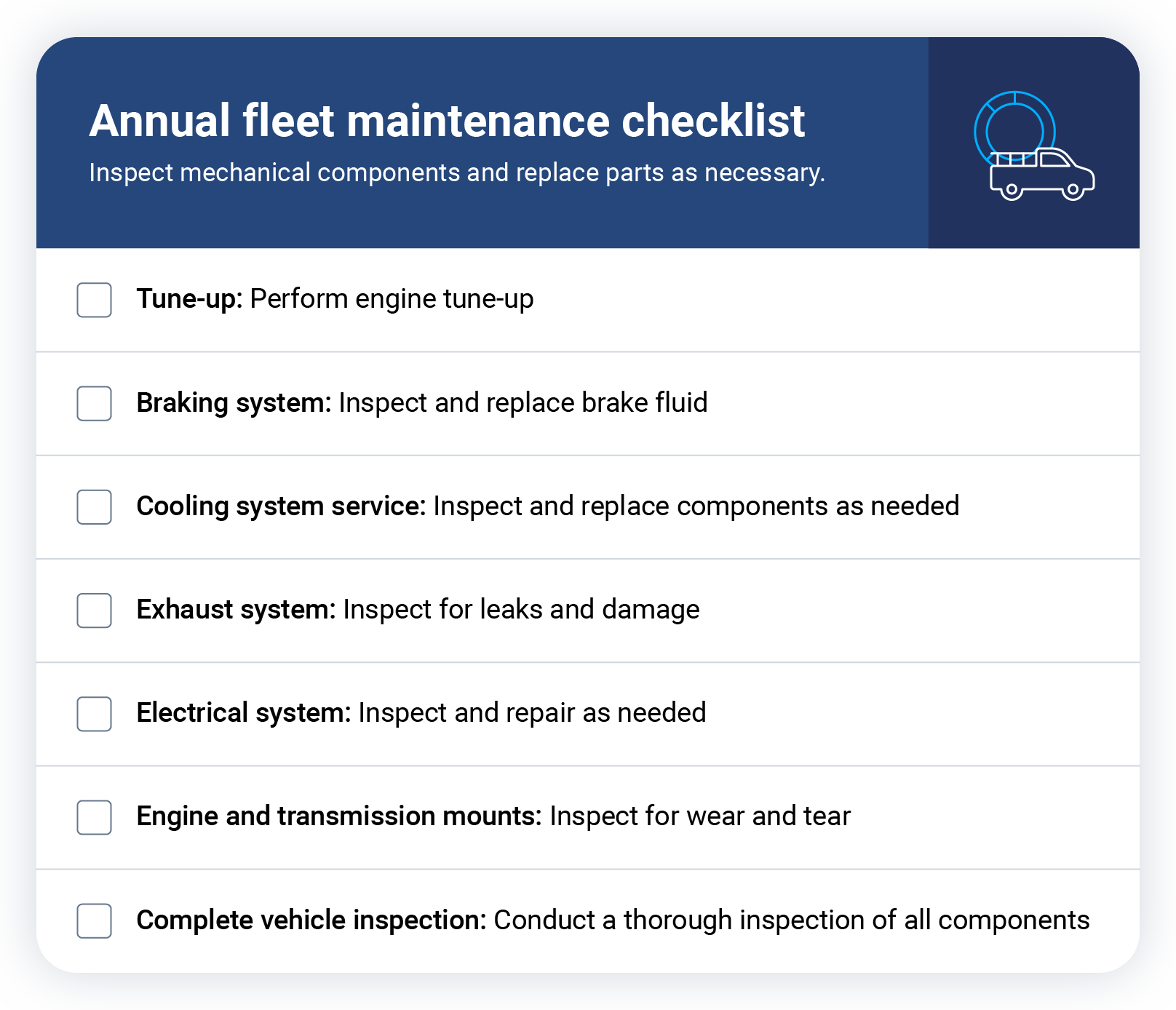
Annual maintenance checklist
Key vehicle parts, like the transmission and electrical systems, must be checked during yearly tune-ups. By this time, some parts might need repairs.