What is ADAS?
ADAS are in-vehicle technologies designed to enhance vehicle safety and assist the driver in better controlling the vehicle.
By Geotab Team
Jan 12, 2024
Updated: May 28, 2024
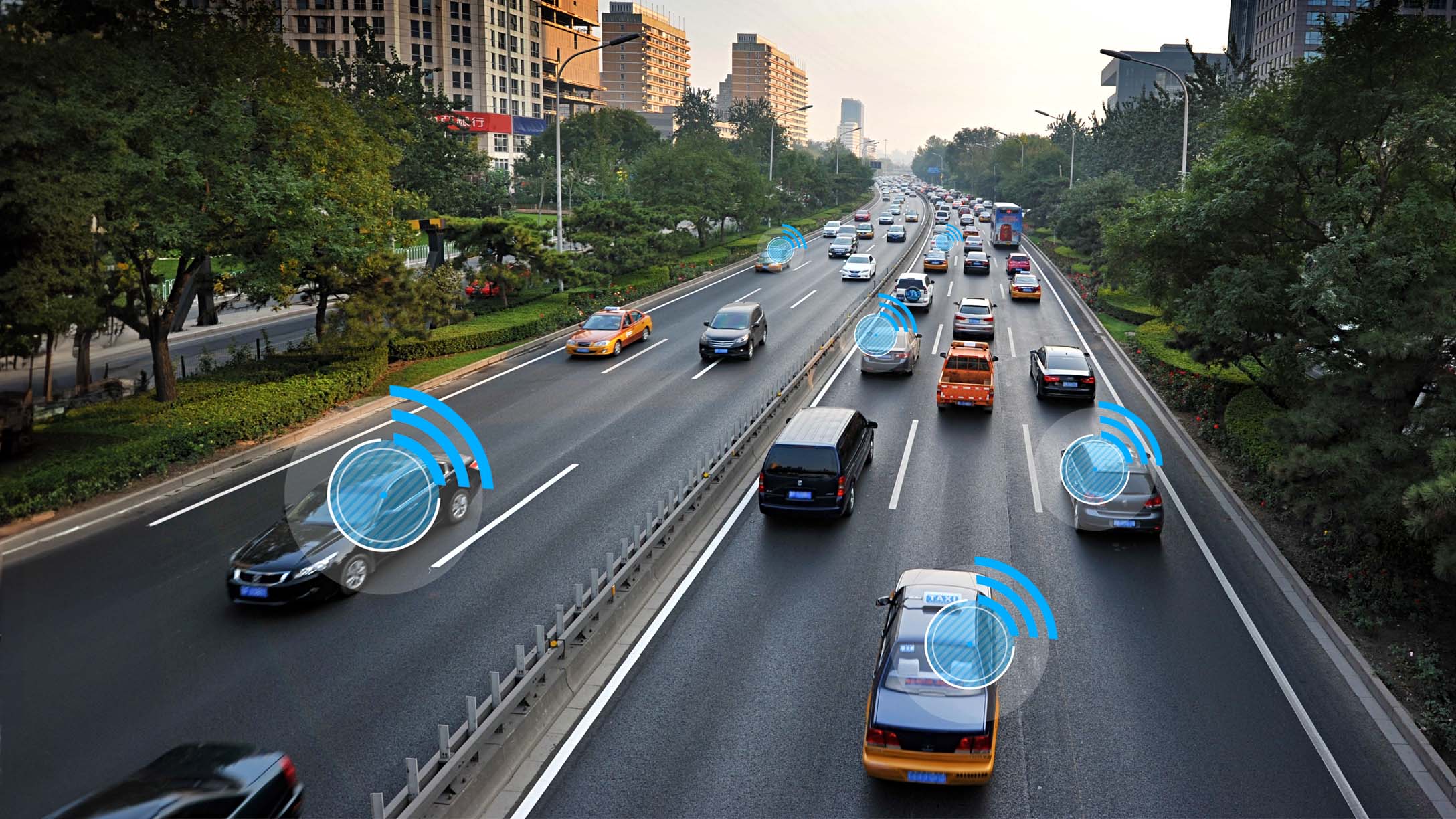

What is ADAS and how does it work?
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are in-vehicle technologies designed to enhance vehicle safety and assist the driver in better controlling the vehicle. These systems do this by alerting the driver to potential problems or taking over specific driving tasks. The primary beneficiaries of ADAS are drivers, passengers and pedestrians. Driver assistance systems work to reduce the number of collisions, thereby increasing overall road safety.
Driver assistance has changed significantly over the past 50 years, from the days of anti-lock brakes to now. Automakers adopting electronic stability control and adaptive cruise control in the 1990s were game changers in vehicle safety. Shortly after, in 2008, Volvo introduced the City Safety system, one of the first autonomous emergency braking systems. Today, ADAS encompasses several safety features that rely heavily on technology. It’s a complex puzzle with lots of moving parts, which can include:
- Sensors: These detect nearby objects or changes in driving conditions. For example, radar sensors can help with adaptive cruise control and collision detection, and temperature sensors can detect changes in weather conditions that might affect the vehicle.
- Cameras: Cameras capture images that the system can then analyze. They are vital for lane departure warnings, traffic sign recognition and pedestrian detection.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses pulsed laser light to measure distances and create detailed maps of the vehicle's surroundings. This enhances features like autonomous parking and adaptive cruise control.
- GPS: Global Positioning System technology factors into navigation systems to provide real-time location information.
- Software algorithms: These are critical for interpreting the data collected by the sensors and cameras, and making decisions based on that information.
ADAS offerings have improved significantly over the past few decades, to the point that many features come standard on most new vehicles. Let’s take a look at some of the most common ADAS safety features.
Popular ADAS Applications
Adaptive Cruise Control
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) is an automatic function that adjusts a vehicle’s speed to maintain safe distances from traffic ahead of them. Mitsubishi introduced it in 1992 as its “Debonair” distance warning system. In 1999, Mercedes-Benz introduced radar-assisted ACC on its S-Class and CL-Class vehicles.
Today, most ACCs use radar and sometimes LiDAR sensors to detect vehicles in front and adjust speed accordingly. This feature has become increasingly common, with many mid-range and luxury vehicles now offering it as standard or optional.
Lane Keeping Assistance
Lane Keeping Assistance (LKA) — sometimes called lane departure warning systems — helps prevent unintentional lane departures. When the system detects unintentional movement out of its lane, it causes the steering wheel or seat to vibrate to alert the driver. In some cases, it may sound an audible alarm. Some LKA systems even act by automatically steering the vehicle back into its lane.
Collision Avoidance Systems
Collision Avoidance Systems, also known as Pre-Collision Systems, use radar, fleet dash cameras and other sensors to detect potential collision scenarios in advance and alert the driver. If the driver does not respond, some systems can automatically apply the brakes to prevent or mitigate a collision. Volvo pioneered this technology, introducing the City Safety system as standard in 2010.
Parking Assistance
Parking Assistance systems help drivers park more easily. Some systems can detect a suitable parking space and instruct the driver when to shift gears and apply gas or brakes. Others can even take over the steering to park the vehicle. Toyota introduced an automatic parking system in 2003 and now many vehicles include this feature.
Blind Spot Detection
Blind Spot Detection systems warn drivers of vehicles in blind spots during lane changes or when vehicles are approaching from behind at high speeds. These systems typically use radar or ultrasonic sensors to monitor areas the driver cannot see easily. Volvo introduced this technology in 2005 with its Blind Spot Information System (BLIS).
Benefits of ADAS in fleet management
The widespread adoption of vehicles with ADAS has plenty of benefits for fleet safety. ADAS technologies like collision avoidance systems, lane departure warnings and adaptive cruise control reduce the risk of collisions by alerting drivers to potential hazards and, in some cases, even taking control of the vehicle to prevent collisions.
ADAS is also great for driver awareness. Blind spot detection and forward collision warnings help keep drivers aware of their surroundings and promote safer driver habits. Advanced driver drowsiness detection can alert fleet managers if drivers show signs of fatigue, allowing them to take action before incidents happen. This has enormous implications for fleet compliance and driver coaching, enabling real-time conversations.
Using ADAS for fleet management has a financial impact, too. Insurance companies reduce insurance premiums for vehicles with ADAS because they decrease collision risk. That can translate to substantial savings for fleet owners. Fewer incidents lead to fewer repairs, further cutting costs. Finally, adaptive cruise control and eco-driving support can improve fleet fuel efficiency, which can help with your business’s fleet sustainability efforts. The less money you spend fueling your fleet, the more you can spend elsewhere.
In addition to these benefits, ADAS can also enhance a fleet's reputation. A company that uses advanced safety technology may appear more responsible and dedicated to the welfare of its employees and the public. This can lead to increased business opportunities and customer trust.
In conclusion, we can’t overstate the importance of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems for fleet management. These systems enhance the safety of both drivers and other road users while providing significant financial benefits for fleet owners.
What is the future of ADAS?
In order to understand what the future of ADAS may look like, it's important to understand how automakers and regulatory bodies categorize ADAS into different levels based on how much automation is present. ADAS are classified in the following way:
- Level 0: At this level, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems do not control the vehicle, but provide information for the driver to interpret. Features at this level include lane departure warnings, blind spot cameras and forward collision warnings. Most vehicles on U.S. highways are Level 0.
- Level 1: Known as driver assistance, Level 1 ADAS can assume control of a single function within the vehicle. Features in this category include adaptive cruise control and emergency brake assist.
- Level 2: With Level 2 ADAS, the system can control multiple functionalities, including autonomous parking. The vehicle is partially autonomous but still requires human monitoring at all times.
- Level 3: Level 3 ADAS can manage most of the vehicle's functions, though human intervention is still necessary. Vehicles with Level 3 ADAS have environmental detection capabilities, allowing them to perform tasks such as accelerating past a slow-moving vehicle.
- Level 4: This level signifies high driving automation. The ADAS at this level is advanced enough that human override is typically unnecessary in most situations. Waymo’s self-driving taxi fleet in Arizona and San Francisco qualify as Level 4 ADAS vehicles.
- Level 5: The highest level of ADAS, Level 5, allows for full vehicle autonomy. Human interaction, including hand control on the wheel, becomes optional. Vehicles with Level 5 ADAS may not need a steering wheel or pedals.
It’s an exciting time for ADAS as manufacturers focus on enhancing safety and convenience. Experts predict the autonomous vehicle market at levels 3 and 4 may reach $6 billion by 2023, reflecting increased demand. Future ADAS will likely incorporate augmented reality (AR) to provide drivers real-time data overlaid within their line of sight.
The next generation of ADAS promises to increase safety for motorists and pedestrians alike, especially in the context of electric vehicles. As automakers introduce more technologies, we’ll see enhancements to safety and efficiency. There’s even more enthusiasm for autonomous vehicles in the commercial sector, especially as cutting costs and improving efficiency become bigger priorities.
In the long run, ADAS isn’t just transforming the driving experience for commuters and commercial drivers – it’s playing a crucial role in enhancing road safety for everyone.
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
The Geotab Team write about company news.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts

What is DEF? How diesel exhaust fluid works and why it's essential for fleets
July 16, 2025
5 minute read

Odometer reading: How to check + optimize for smarter fleet management
July 15, 2025
5 minute read

9 strategies to increase fleet fuel efficiency and lower fuel costs
July 8, 2025
4 minute read

Creating a fleet safety culture that’s built to last: Lessons from Missouri DOT and NYC
July 7, 2025
8 minute read