CARB States: A guide to understanding emissions regulations in the U.S. [2025]
Diesel trucks are a major pollution culprit, but a growing number of states are fighting back with stricter rules.
By Geotab
Jul 17, 2025

Key Insights
- What does CARB stand for? CARB stands for the California Air Resources Board. CARB regulations help improve air quality and reduce the impacts of climate change.
- What is a CARB state? A CARB state is a state that has adopted the strict vehicle emission standards set by the California Air Resources Board.
- What states are CARB-compliant? Over a dozen states have adopted CARB's emissions standards following California's lead, including New York and Massachusetts.
The fact that diesel semi-trucks account for 18% of all U.S. vehicle emissions is a major driver behind the growing movement of states adopting the California Air Resources Board (CARB) environmental standards, collectively known as CARB states.
In CARB states, fleets must adhere to strict emissions requirements, which often necessitates investments in newer, cleaner vehicles, or the adoption of alternative fuels. This can include transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs) or vehicles that use other low-emission technologies.
But what exactly are these strict regulations and which states have adopted CARB policies?
What is CARB?
CARB stands for the California Air Resources Board. It's a state agency tasked with protecting public health and the environment by regulating air pollution. Being CARB-compliant means adhering to the emissions standards set by this board, which are often stricter than federal regulations. These standards aim to reduce pollutants from various sources, with a significant focus on vehicles.
For fleets operating in CARB states, compliance often involves transitioning to cleaner vehicles, such as electric vehicles, and employing telematics software to track vehicle data. CARB regulations can necessitate investments in new technologies, adjustments to maintenance schedules and careful route planning to minimize emissions.
The requirements vary depending on the type and size of the fleet, but generally involve meeting specific emissions targets and reporting data to ensure compliance.
EPA vs. CARB: What’s the difference?
The EPA and CARB both regulate air pollution but operate at different levels. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is a federal agency that sets national standards for air quality and vehicle emissions that must be met by all vehicles in the U.S.
In contrast, the California Air Resources Board is a state agency that establishes its own, often stricter, emissions regulations. This has led to several other states choosing to adopt CARB regulations on top of existing federally mandated EPA policies.
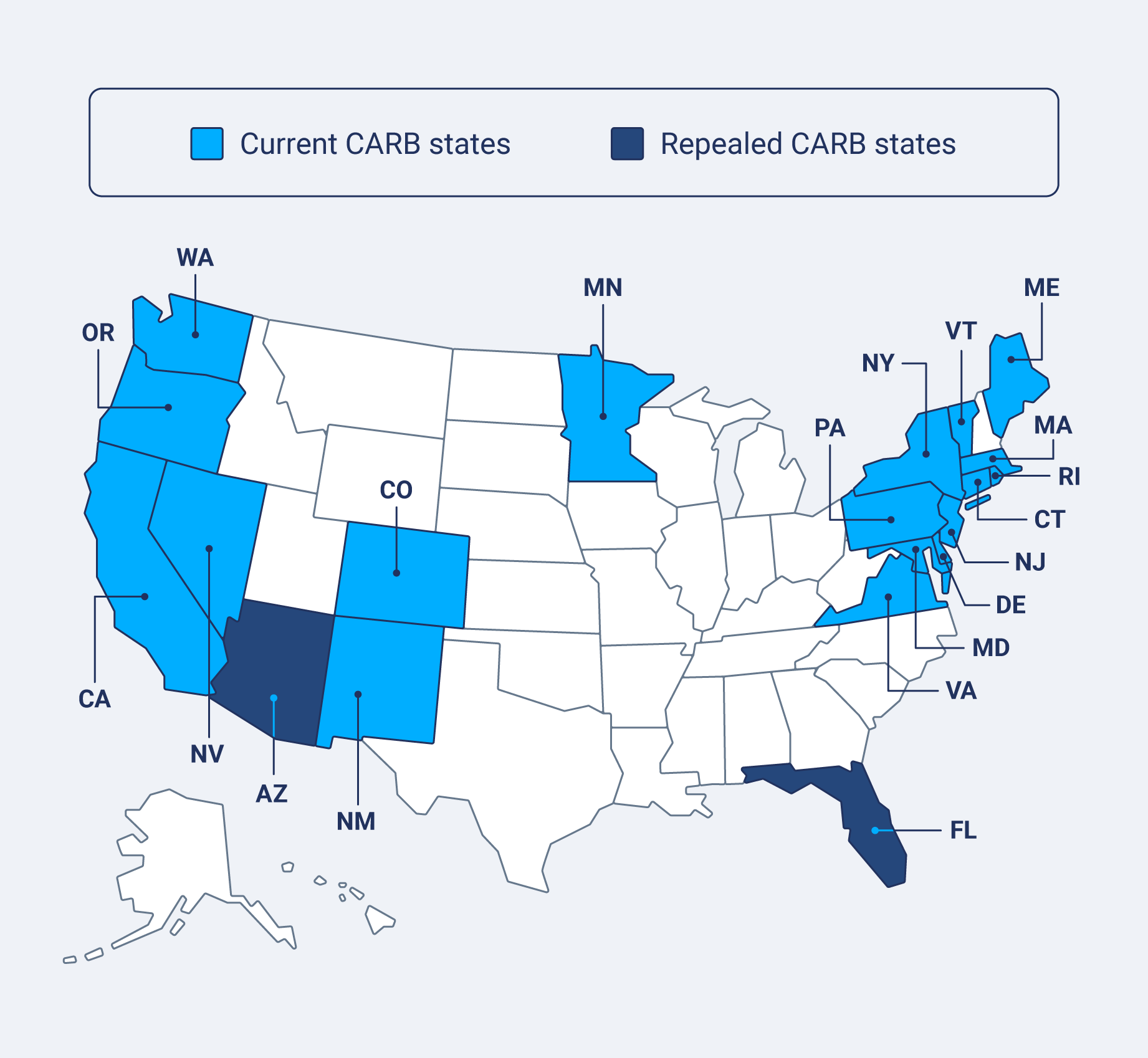
CARB-compliant states
CARB-compliant states are those that have adopted California's stringent vehicle emissions standards, aiming to reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. These states recognize the importance of cleaner vehicles for public health and environmental protection.
Current CARB states:
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Minnesota
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
While most states are moving toward stricter emissions regulations, some states have repealed previous CARB adoption.
Repealed CARB states:
- Arizona
- Florida
Fleet CARB regulations examples
CARB regulations significantly impact fleet operations, pushing for cleaner vehicle technologies and reduced emissions. Here are some key regulations fleets operating in CARB states should be aware of:
- Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) Rule: This rule mandates manufacturers to increase the production and sales of zero-emission trucks, gradually shifting the market towards cleaner heavy-duty vehicles.
- Advanced Clean Fleets (ACF) Rule: The ACF rule requires fleets, especially large ones, to transition to zero-emission vehicles for their operations, setting specific timelines and targets for this transition.
- Truck and Bus Regulations: These regulations focus on reducing emissions from existing heavy-duty diesel trucks and buses, often through engine upgrades, retrofits or the replacement of older vehicles.
- Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Requirements: These requirements set specific percentages of zero-emission vehicles that must be included in a fleet's overall makeup, accelerating the adoption of electric and other clean technologies.
| Light-Duty Vehicle Standards | Heavy-Duty Vehicle Standards |
|---|---|
| Advanced Clean Cars | Advanced Clean Trucks |
| LEV Criteria Pollutant | Heavy-Duty Omnibus |
| LEV Greenhouse Gas | Phase 2 Greenhouse Gas |
| Zero-Emission Vehicle |
It's important to note that specific regulation requirements can vary by state, and the CARB states chart below indicates which regulations apply in each location.
| State | ZEV state | LEV state | ACT state |
| California | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Colorado | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Connecticut | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Delaware | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Maine | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Maryland | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Massachusetts | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Minnesota | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Nevada | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| New Jersey | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| New Mexico | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| New York | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Oregon | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Pennsylvania | - | ✅ | - |
| Rhode Island | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Vermont | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Virginia | ✅ | ✅ | - |
| Washington | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Washington D.C. | ✅ | ✅ | - |
Compliance strategies for CARB-state fleets
Navigating CARB compliance can be complex for EV fleet managers. Proactive strategies are essential to stay up to date on regulations and minimize operational disruptions. This involves everything from regular audits and strategic planning to leveraging financial incentives and investing in alternative fuel infrastructure.
For diesel fleets, this may also include consistent use and monitoring of diesel exhaust fluid, which is essential for meeting CARB’s strict NOx emissions standards.
Here are some key compliance strategies for fleets operating in CARB states.
1. Conduct regular fleet audits
Regular fleet audits are crucial for assessing current emissions levels and identifying areas for improvement. This involves evaluating the age and condition of vehicles, analyzing fuel consumption and monitoring maintenance records.
Audits help fleet managers understand their compliance status and pinpoint necessary adjustments to meet CARB standards. In addition, utilizing telematics devices and fleet management software helps streamline the process by easily comparing your current fleet data to zero emissions goals.
2. Develop a clear CARB-compliance timeline
Creating a detailed compliance timeline is essential for a smooth transition. This timeline should outline key milestones and reporting deadlines. More specifically, it's a good idea to break down the timeline into actionable phases, including research and evaluation of ZEV options, procurement of new vehicles, infrastructure installation and staff training.
A clear timeline allows fleet managers to plan their investments and operations effectively, ensuring they meet CARB requirements without last-minute scrambling.
3. Utilize available incentives and grants
CARB states often offer incentives and grants to support fleets in their transition to cleaner technologies. For example, California’s HVIP (Hybrid and Zero-Emission Truck and Bus Voucher Incentive Project) provides vouchers to reduce the upfront cost of purchasing hybrid and zero-emission trucks and buses to combat smog.
But beyond California’s HVIP, several different incentives and federal programs may apply. Leveraging these grants can significantly reduce the financial burden of compliance and help you weigh the long-term benefits of minimizing emissions.
4. Invest in alternative fuel infrastructure
Transitioning to alternative fuels, such as electricity or hydrogen, requires careful planning and infrastructure investment. This means thoroughly evaluating each fuel's benefits prior to installing charging or refueling stations.
Strategic investment in infrastructure ensures that fleets can efficiently operate their alternative fuel vehicles and meet CARB’s emission requirements.
5. Train drivers and fleet managers
Proper training is essential for the successful implementation of CARB compliance strategies. Drivers and fleet managers need to understand the new regulations, operate alternative fuel vehicles efficiently and adopt best practices for emissions reduction.
Training programs should cover topics such as vehicle maintenance, fuel efficiency and compliance reporting.
Trust Geotab to bring your fleet to the future
As environmental concerns escalate, more and more states are adopting the emissions standards pioneered by CARB, making it crucial for fleets nationwide — and even worldwide — to prepare for these changes.
Beyond simply complying with CARB states' requirements, embracing cleaner technologies and practices is becoming essential for long-term operational viability and environmental responsibility.
Geotab's fleet management software empowers fleets to monitor and manage emissions, optimize fuel consumption and track vehicle performance, all critical aspects of CARB-compliance solutions. In fact, Geotab is the only provider with both a CARB Clean Truck Check Certification and T-harness installation exemption, ensuring seamless compliance with the Heavy-Duty Vehicle Inspection and Maintenance (HD I/M) Regulation.

Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Frequently Asked Questions
A CARB state is a state that has adopted the stricter vehicle emissions standards set by the California Air Resources Board.
CARB-compliant means adhering to the stringent emissions standards established by the California Air Resources Board.
There are currently 18 CARB states, as well as two states that have repealed their CARB status.
ZEV states are states that have adopted California's Zero Emission Vehicle program, mandating a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be zero-emission vehicles. These states include:
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- District of Columbia
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Minnesota
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- Oregon
- Rhode Island
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
Geotab team
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts


Best ELD for trucks: Top devices for compliance and safety [2026]
December 18, 2025
6 minute read


Best ELD for owner operators: Top 6 picks and how to choose one
December 1, 2025
6 minute read


Infographic: Upgrading your cold chain solution to minimize waste and maximize profit
September 11, 2025
1 minute read