The Geotab GO7 certification process
Automotive electromagnetic compliance tests as per the specifications of the relevant international associations.
As the end user of a GO7, perhaps you’ve wondered what steps it took to get the device in your hands and into your automobile. As you can imagine, your device went through a complex process involving tests, certification and compliance, before being accepted for use by your carrier. The exact test and certification process depends on your carrier and location but generally follows the following procedure.
Pre-certification Tests
Before certifying the GO7, Geotab carried out a series of exhaustive tests to check for compliance. These tests include the following:
Automotive electromagnetic compliance tests as per the specifications of the relevant international associations, SAE and CISPR(International Special Committee on Radio Interference) including:
- Inductive switching
- Burst transients
- Starter motor engagement
- Electrical fast transient burst
- Electrostatic discharge
- Radiated immunity
- Radiated emissions
- Conducted emissions
Environmental tests:
- Operation and functioning (-40℃ to +85℃)
- Thermal shock
- Mechanical vibration
- Operational shock
Radio frequency tests:
- Conducted and OTA (over-the-air) pre-tests to ensure that the RF performance meets specified limits
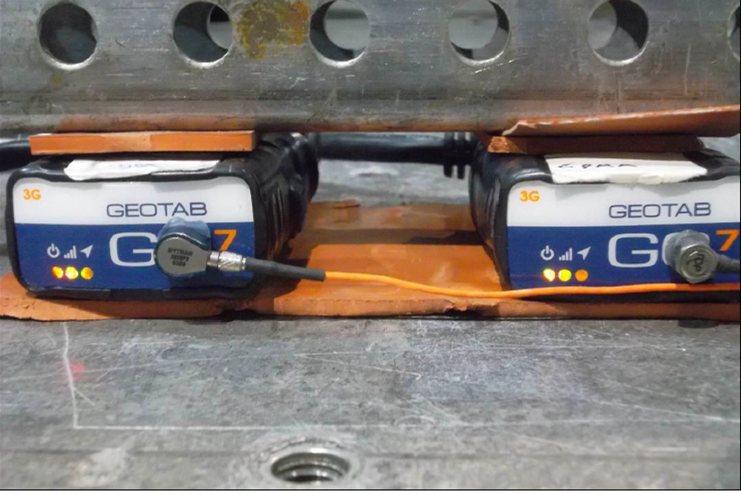
Mechanical Vibration Test

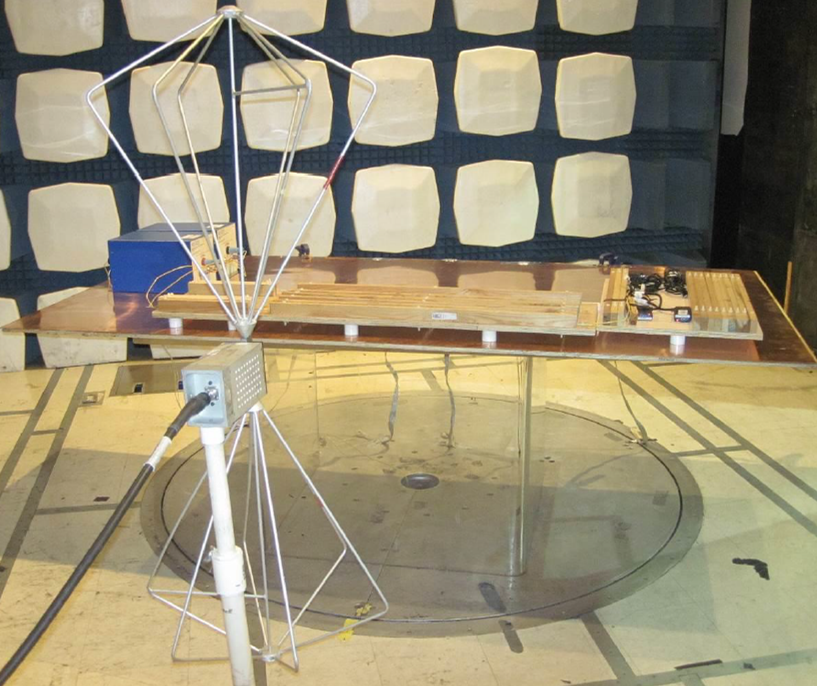
Radiated Emissions Test
Sample Submission
Samples are required to be submitted to carrier-approved labs or carrier labs for the test and certification. In some cases, the labs would need firmware to be modified to an engineering version, which gives control over the device. In other circumstances, samples might need the internal antenna to be removed and replaced with radio frequency compatible cables and connectors.
Certification in the U.S
The requirements for any region can be broadly divided into those enforced by government agencies, industry agencies and carriers. U.S. certification requirements for the GO7 are summarized below – the tests are applicable mainly to 2G and 3G devices. For CDMA devices, which do not need PTCRB (certification body in North America) approval, a subset of the tests is used – FCC (Federal Communications Commission) Part 15B, RF performance and carrier certification. Other regions follow a similar process and have requirements of their own governmental agencies. For example, Industry Canada and CE (Europe).
Government Requirements
In the U.S., the FCC has requirements that the GO7 must comply with. Part 15B is mandatory for all GO7 versions, while Parts 2, 22H, and 24E are applicable only to GO7 2G and 3G versions.
FCC certification (Part 15B) tests for unintentional radiators.
FCC certification (Parts 2, 22H, 24E) tests for the following:
- Conducted power
- Peak-to-average ratio of RF transmission
- Effective radiated power/Effective isotropic radiated power
- Bandwidth measurements
- Band-edge measurements
- Conducted spurious emissions
- Field strength of spurious radiations
- Frequency stability
Industry Requirements
PTCRB was set up by the cellular industry to ensure compliance to carrier standards. Most carriers require PTCRB certification, with the exception of those using CDMA technology. PTCRB certification entails the following tests:
- Conformance tests to 2G and 3G technology (including idle mode, radiated spurious emissions-intentional, receiver flatness, SIM tests)
- Specific absorption ratio (human exposure to RF radiation)
Radio frequency performance:
- Total radiated power (TRP): a measure of the RF power transmitted
- Total isotropic sensitivity (TIS): a measure of sensitivity to received RF signals
Pass/fail RF criteria of the carrier must be met where specified.
Carrier Requirements
Most carriers perform additional tests to ensure that the device works seamlessly with their network. In some cases, this might require firmware changes and re-testing until the carrier’s requirements are met.
The rigorous test methodology ensures that the GO7 device you use is of the highest level of quality and reliability. The GO7 is currently certified for use with major carriers such as Verizon, Sprint, Rogers, Telus, and Telefonica, while certifications in Australia and Singapore are ongoing.
To learn more about the certification of any Geotab devices, leave a question or comment in the comments box below!
See Also:
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
The Geotab Team write about company news.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts

Enhancing winter road maintenance with postseason materials usage analyses
June 20, 2025
6 minute read


The ROI of telematics for truck lessors: Turn data into profit
May 27, 2025
3 minute read

CARB compliance made easy: 10 ways Geotab simplifies emissions reporting
May 12, 2025
1 minute read


IRS mileage log requirements for 2025 [free downloadable template]
May 2, 2025
5 minute read