What is predictive maintenance (PdM)? Benefits, challenges & examples for fleet management
Predictive maintenance could be the key to avoiding breakdowns and expensive repairs.
By Geotab Team
Sep 12, 2024
Updated: Nov 27, 2024

Key Insights
- Predictive maintenance (PdM) uses data to predict when fleet vehicles need repairs.
- Using data-driven insights, PdM can help reduce maintenance costs and boost vehicle uptime.
- While preventative maintenance can lead to unnecessary maintenance if the asset does not need repair, PdM only focuses on assets that require attention.
Have you ever been caught off guard by an unexpected truck breakdown? Or perhaps faced a costly repair that disrupted your fleet's operations? Predictive maintenance (PdM) offers a proactive solution.
By harnessing the power of data-driven insights, PdM empowers you to transform your fleet operations. Instead of reacting to breakdowns, you can anticipate and address fleet maintenance needs proactively.
Predictive maintenance is the key to avoiding breakdowns and expensive repairs. By capturing and utilizing the right vehicle data, you can optimize maintenance schedules, reduce downtime and improve overall fleet performance. Let's explore the importance of PdM for your fleet.
What is predictive maintenance?
Predictive maintenance uses data and analytics to predict potential equipment failures, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly breakdowns. In its simplest form, PdM is important because it leverages real-time, customized telematics data to identify vehicle or truck failures before they occur across all Class 1-8 vehicles.
A predictive fleet maintenance solution takes hundreds of thousands of vehicle data points, such as sensor data and driver usage, and then learns from analyzing the vehicles across all asset classes to pick out patterns that have led to distinct failures in the past. It then alerts the fleet manager in real-time, of a potential failure weeks before it will actually happen.

How does predictive maintenance work?
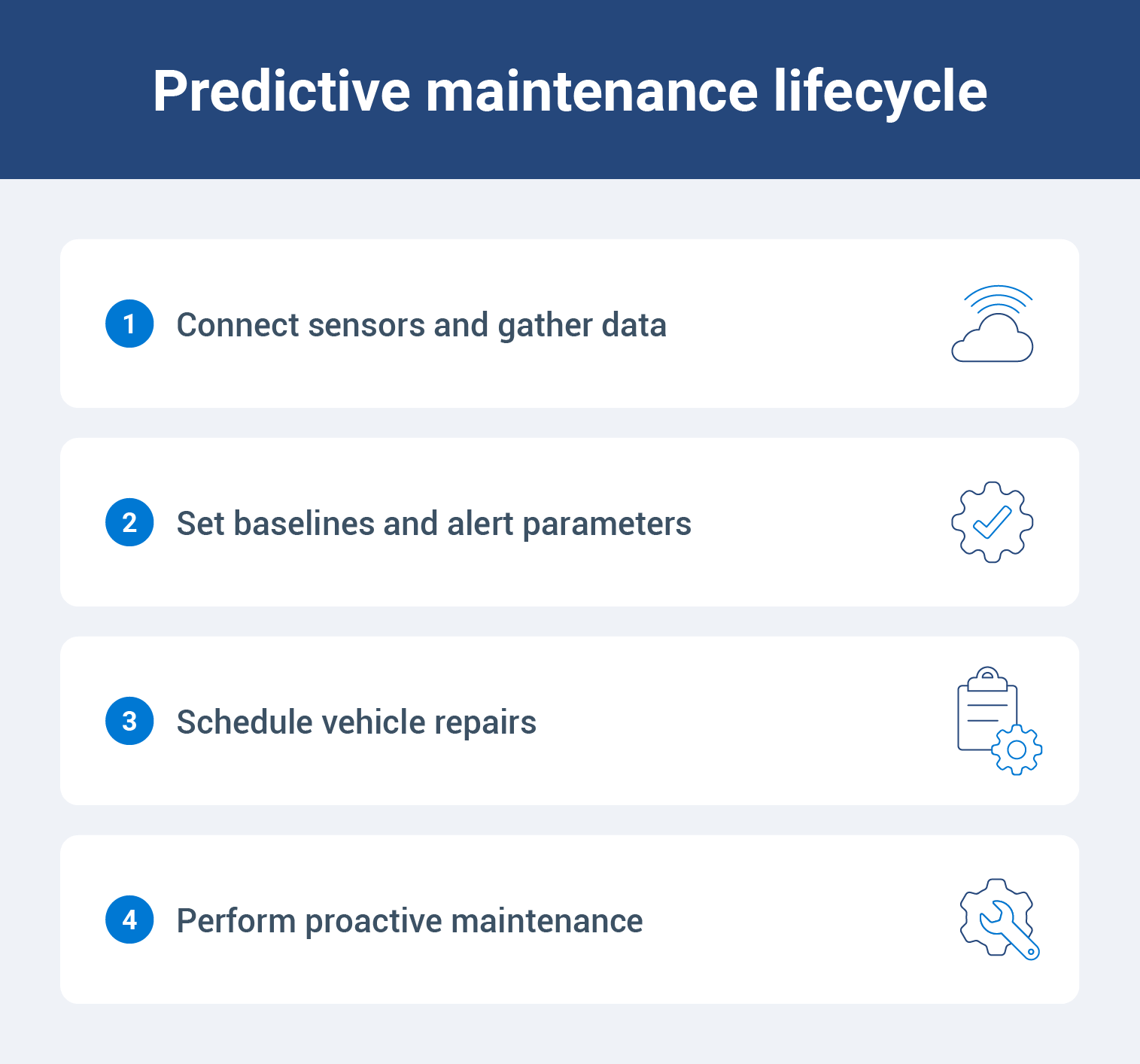
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data to predict when a vehicle needs to be repaired. Yet, people often misunderstand the process. Predictive maintenance is so much more than using past work order history to make assumptions about the future. It’s a complementary approach to preventive maintenance that helps fleets avoid costs between cycles.
The predictive maintenance process collects data to detect baseline deviations, triggering a maintenance work order. Predictive maintenance solutions aim to optimize vehicle uptime, reduce maintenance costs and improve overall fleet efficiency by:
- Accurately predicting equipment failures before they occur
- Prioritizing maintenance tasks based on urgency and failure risk
- Optimizing inventory management through precise forecasting
- Extending asset lifespan through early detection and mitigation of issues
- Enhancing fleet safety by preventing breakdowns that could lead to collisions
Benefits of predictive maintenance in fleet management
Proper vehicle maintenance is essential for your fleet's safe and efficient operation. But did you know that it can also improve fuel economy? With pump prices skyrocketing, a predictive maintenance program with telematics data can provide substantial fuel and repair savings to reduce operating costs. Let’s look at the top predictive maintenance advantages and disadvantages.
| Pros | Cons |
| Eliminates surprise repairs | Can be difficult to implement |
| Reduces shop visits | Requires driver training |
| Improves fleet safety | Challenging to capture the right data |
| Boosts fuel efficiency | Difficult to know when to use predictive vs. other types of maintenance |
| Increases vehicle lifespan | |
| Reduces CVSA violations | |
| Boosts driver retention |
Eliminates surprise repairs
Surprise repairs can lead to unexpected vehicle downtime, causing disruptions and increased costs. Predictive maintenance offers a solution by identifying potential issues before they become critical.
For example, one study found that when a logistics fleet implemented a predictive maintenance platform, it could quickly identify several underperforming trucks. The platform revealed potential battery and brake failures and other maintenance needs. This proactive approach allowed the fleet manager to prioritize critical repairs and avoid costly, unscheduled downtime.
Reduces shop visits
Predictive maintenance reduces the need for emergency repairs and streamlines routine maintenance. By anticipating necessary tasks, fleet managers can schedule multiple services at once, minimizing the number of shop visits. For instance, combining an oil change with a coolant flush can save time and money.
With predictive maintenance, a fleet manager can keep the trucks on the street by booking ahead of time to ensure the vehicle is in the shop once rather than twice.

Improves fleet safety
Predictive maintenance can help improve the safety of your fleet. Brake predictions allow a fleet manager to remotely detect a vehicle's health and ability to stop at a reasonable distance. Worn-out brake pads cause longer stopping distances, increasing the risk of brake-related collisions.
With predictive maintenance, managers are able to minimize fleet risk by leveraging the vehicle health score and insights and remove any dangerous assets on the street or remarket underperforming ones ahead of the normal replacement cycle.
Boosts fuel efficiency
With pump prices skyrocketing, a predictive maintenance program with telematics data can provide substantial fuel savings to reduce operating costs.
- Engine oil: Low engine oil levels can lead to increased friction and strain on the engine, resulting in reduced fuel efficiency.
- Intake and exhaust systems: Clogged or damaged intake and exhaust systems can impact fuel efficiency.
- Engine cooling: A constantly running cooling fan can reduce fuel efficiency.
- Air compressors: Excessive air compressor operation can result in a loss in fuel economy.
- Wheel alignment: Misaligned wheels increase rolling resistance, making trucks work harder and consuming more fuel.
- Tires: Underinflated tires can decrease fuel economy by 2% for every 10 PSI of underinflation. Overheating and blowouts are also more likely.
- Fuel filter systems: Clogged fuel filters can restrict fuel flow, straining fuel pumps and leading to excess fuel consumption.
- Aerodynamic devices: Class 8 trucks spend 50% of their fuel overcoming air resistance on highways. Ensuring aerodynamic devices are damage-free is crucial for fuel efficiency.
- Electrical systems: Malfunctioning batteries, starter motors or alternators can negatively impact fuel economy.
- Air conditioning: A malfunctioning system may run longer than necessary, wasting fuel.
Increases vehicle lifespan
Predictive maintenance extends the life of your vehicles by identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into major breakdowns.
By detecting wear and tear early on, you can schedule repairs and replacements proactively, preventing catastrophic failures that can shorten a vehicle's life span. Allocating resources to predictive maintenance is a strategic move that enhances your fleet's durability and maximizes your overall return on investment.
Reduces CVSA violations
Approximately 4 million commercial motor vehicle inspections are conducted annually through the Commercial Vehicle Safety Alliance (CVSA) to ensure road safety. Predictive maintenance helps prevent common CVSA inspection violations such as brake system failures, tire wear and engine malfunctions. Proactively addressing potential issues can significantly reduce the risk of out-of-service violations, leading to costly downtime and revenue loss.
Implementing predictive maintenance safeguards your fleet’s operational efficiency and demonstrates a strong commitment to road safety.

Increases driver retention
A safe vehicle is a well-maintained vehicle, and a well-maintained vehicle is a reliable one. These truths not only save money for the carrier but also provide the right environment for driver retention.
No driver likes breakdowns — the time, the hassle and the loss of income if paid per mile. A poorly maintained fleet will be at a significant disadvantage when retaining drivers and acquiring new ones.
Challenges of implementing predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance can help lower costs and streamline operations, but it also comes with challenges. Knowing how to implement predictive maintenance technology and capture the right data is key to a successful maintenance program.
The top challenges when putting a predictive maintenance process in place include:
- Implementing system infrastructure: You need the right tools to implement a predictive maintenance program, which means researching and purchasing necessary equipment and technology. For example, if reducing vehicle downtime is important to your fleet, you’ll need a tool that provides real-time insights to integrate with your fleet maintenance checklist.
- Distributing training and resources: Ensuring that fleet drivers and technicians can effectively monitor and respond to maintenance alerts is crucial for the success of your predictive maintenance program. You’ll likely need training around interpreting, troubleshooting and reporting maintenance alerts.
- Capturing the right data: Choosing fleet maintenance software often hinges on its data-capturing capabilities. With so many metrics available, determining the most valuable data can be challenging. Fuel consumption, maintenance schedules and compliance data are some crucial data points to track.
- Knowing when to use predictive analytics: Predictive maintenance is often preferred to preventative maintenance, but there is a time and place for each. While predictive maintenance offers data-driven insights for more accurate predictions, it's important to consider your fleet’s specific needs. Based on fixed intervals, preventive maintenance can be effective for certain assets or when predictive analytics infrastructure costs are prohibitive.
Predictive maintenance examples and use cases
Implementing a predictive maintenance program sounds promising, but how will this look when implemented? Here’s how to use predictive maintenance based on common examples and use cases.
Transportation and logistics
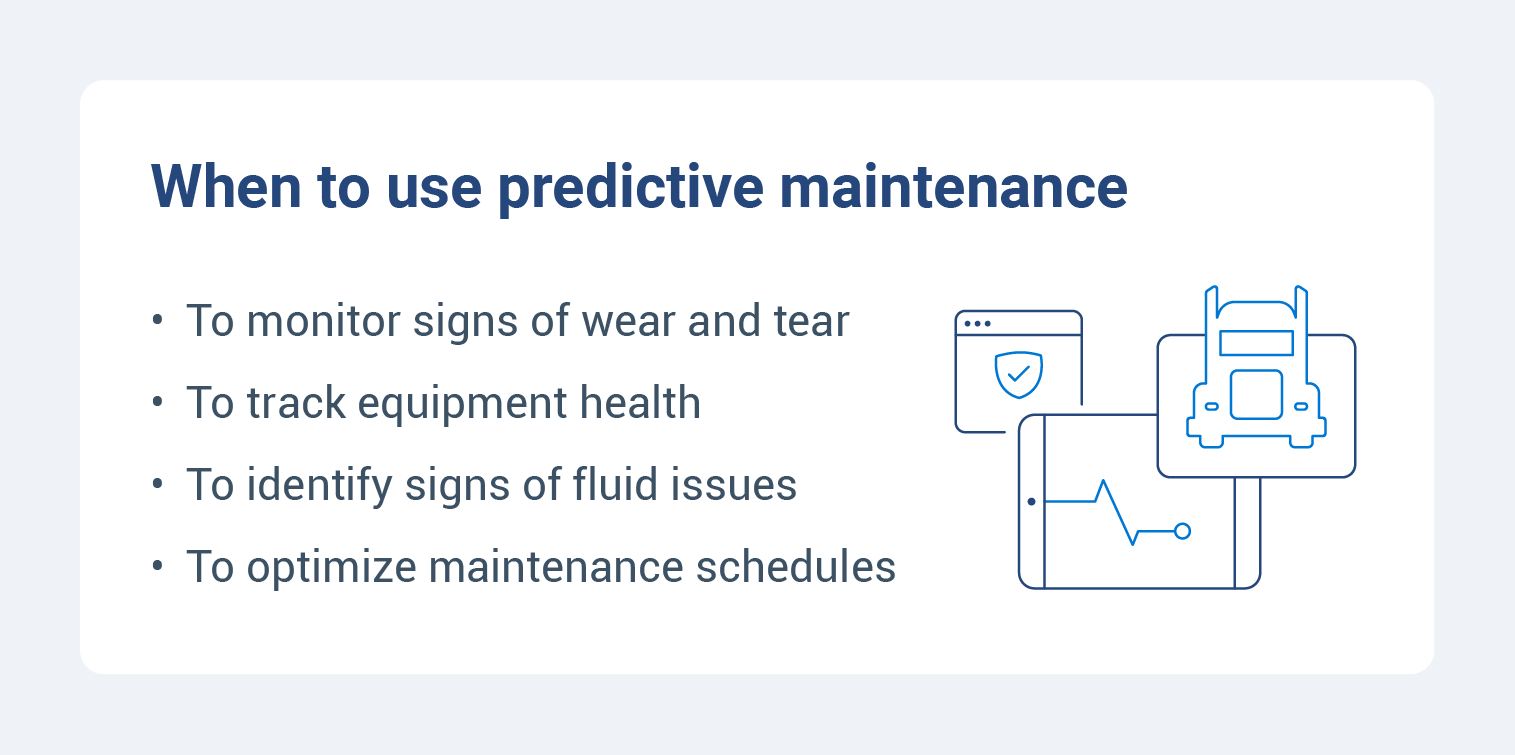
In the fleet transportation and logistics sector, predictive maintenance is essential for maintaining fleet uptime and reducing operational costs. By monitoring vehicle sensors for signs of wear and tear, such as engine temperature, tire pressure and brake performance, fleet managers can proactively schedule maintenance, preventing unexpected breakdowns that disrupt delivery schedules and lead to customer dissatisfaction.
For example, a trucking company can use predictive maintenance to analyze engine vibration data, identifying early signs of bearing failure. By scheduling preventive maintenance, the company can avoid a costly engine overhaul and ensure uninterrupted operations.
Construction
Predictive maintenance is also crucial for fleet construction equipment, where downtime can significantly impact project timelines and budgets. By monitoring sensors on heavy machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers and cranes, construction companies can track equipment health, detect potential failures and schedule maintenance accordingly.
For example, a construction firm can use predictive maintenance to analyze vibration data from an excavator's hydraulic system, identifying early signs of fluid contamination or pump wear. By proactively addressing these issues, the company can help reduce costly equipment breakdowns and avoid project delays.
Rental and leasing
Maximizing asset utilization and minimizing downtime is paramount in the rental and leasing industry. Predictive maintenance allows rental companies to optimize equipment maintenance schedules, ensuring that assets are available for customers when needed. This both improves customer satisfaction and reduces the risk of costly emergency repairs and equipment replacements.
For example, a rental company can use predictive maintenance to analyze a generator's operating hours and maintenance history and predict when a major overhaul is needed. By scheduling the maintenance in advance, the company can ensure the generator is available for rent when customers need it.
Predictive maintenance vs. other maintenance types
Knowing the difference between predictive maintenance and other types of maintenance, such as reactive and preventive maintenance, is key to knowing what’s right for your fleet. Let’s break down how the different types of maintenance programs work.

Predictive vs. preventive maintenance
Predictive maintenance utilizes real-time data and analytics to predict equipment failures, while preventive maintenance follows fixed maintenance intervals, regardless of asset condition.
The biggest difference between the two is that preventive maintenance aims to extend asset life, which can lead to unnecessary maintenance if the asset does not need repair. In contrast, predictive maintenance focuses on assets that require attention, reducing unnecessary fleet management costs.
Predictive vs. reactive maintenance
As its name implies, reactive maintenance is a response to equipment failures. The issue with reactive repairs is that they can lead to unplanned downtime, increased costs and potential safety risks. This differs from predictive maintenance, which proactively addresses potential issues before they escalate, preventing breakdowns and minimizing disruptions.
Predictive vs. conditional maintenance
Conditional maintenance is based on monitoring equipment performance and scheduling maintenance when specific conditions are met. On the other hand, predictive maintenance goes beyond condition monitoring by using data analytics to predict potential failures, allowing for more proactive and targeted maintenance.
While conditional maintenance can benefit certain assets, predictive maintenance offers a more advanced approach by leveraging data-driven insights.
Boost productivity with predictive maintenance technologies for fleet management
When looking to employ a data-driven approach to fleet management, predictive maintenance offers proactive insights to catch problems early and save time and money. By implementing a predictive maintenance program, fleet managers can predict equipment failure, minimize vehicle downtime and make more informed decisions.
Streamline your maintenance schedule and boost productivity with the right vehicle maintenance software.

Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Frequently Asked Questions
Preventive maintenance is scheduled upkeep based on time or usage, while predictive maintenance uses real-time data to predict when maintenance is needed. While preventive maintenance aims to extend asset life, predictive maintenance focuses on reducing unnecessary maintenance costs.
Predictive maintenance is important because it prevents unexpected equipment failures, reduces downtime and optimizes maintenance costs. Predicting when equipment needs repair allows for scheduled maintenance instead of emergency fixes, improving overall efficiency and reliability.
Predetermined maintenance is another term for preventive maintenance. It involves performing maintenance tasks at fixed intervals, based on time or usage, without considering the actual condition of the equipment.
The Geotab Team write about company news.
Table of Contents
- What is predictive maintenance?
- How does predictive maintenance work?
- Benefits of predictive maintenance in fleet management
- Challenges of implementing predictive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance examples and use cases
- Predictive maintenance vs. other maintenance types
- Boost productivity with predictive maintenance technologies for fleet management
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts

9 strategies to increase fleet fuel efficiency and lower fuel costs
July 8, 2025
4 minute read


Fuel efficiency techniques every truckload carrier should know
May 30, 2025
3 minute read

5 data-driven strategies to optimize your oil and gas fleet
May 29, 2025
2 minute read


Six ways telematics reduces costs for waste management fleets
May 16, 2025
6 minute read