Intro to third-party device integration
With third-party device integration, Geotab has opened up the ability for partner devices to contribute to the rich telematics data in the Geotab platform.

Traditionally, the main device source of telematics data contributing to the Geotab cloud platform were Geotab GO devices (physical devices connected to a vehicle collecting and sending data) or partner vendor devices (connected to a GO device via an IOX expansion cable interface) collecting rich data and passing it through the GO device to Geotab.
Now, Geotab has fully opened up the ability for partner vendor devices, independent of the GO device, to be able to contribute to the rich telematics data residing within the Geotab platform. Geotab calls these devices “third-party devices.” Once third-party telematics devices are integrated, they can be viewed alongside Geotab GO devices through a single MyGeotab interface — allowing third-party telematics devices to take advantage of MyGeotab’s powerful rules engine and reporting capabilities.
See also: The power of PTO connections in telematics
Types of third-party integrations for telematics
Third-party devices can take many forms: software or hardware. One popular method is a software integration implemented by a Geotab Partner who collects telematics data from a device and sends that data to the Geotab telematics cloud platform.
Another way to integrate could be an embedded hardware device that collects data and sends it to the Geotab cloud platform via its own Internet connection.
With third-party device integration, the Geotab cloud platform acts as an IOT hub, bringing the promise of the Internet Of Things (IoT), Platform as a Service (Paas), closer to reality.
How do third-party devices work with the Geotab platform?
The Geotab open platform for telematics is made up of the following components: a telematics device (Geotab GO device or third-party device) communicating through a server or directly with the Geotab Gateway server, which forwards the data to the database for processing and storage. The telematics data can then be viewed by Geotab users using the MyGeotab web application. These are the physical building blocks that make up the Geotab platform and the mechanism via which third-party devices can send data to the platform.
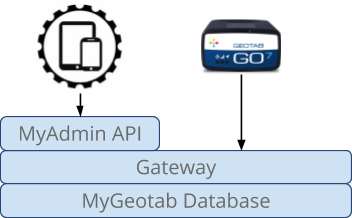
Data is sent to the Geotab platform via telematics devices or APIs.
Add to that our third-party devices and partner systems communicating via the Geotab Application Program Interfaces (APIs) to retrieve stored telematics data, and you can see there is a full cycle of communication between the Geotab customer, their telematics devices, the internet, and the physical world through the Geotab platform — the Geotab IOT Ecosystem.
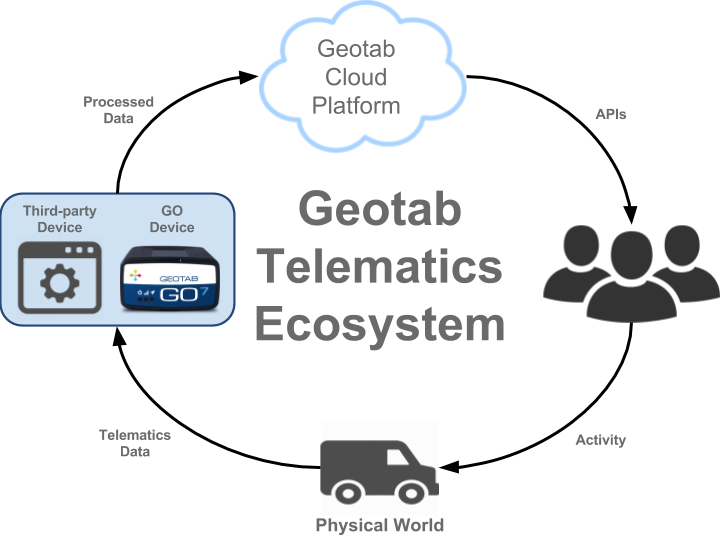
Geotab Telematics Ecosystem
Geotab APIs give Geotab customers the ability to access telematics data via the internet from the Geotab platform for the intention of consuming telematics data via the MyGeotab API or administering their third-party device via the MyAdmin API.
Customers can enrich their fleet operations and asset management by leveraging systems like solar powered asset trackers. Having the ability to manage all of their vehicles and non-powered assets, like trailers, within one software application greatly improves efficiency and the overall user experience.
Deep dive: Third-party device integration
Third-party device communication
For those who want to know more, it should be mentioned that a third-party device communicates via Web requests to the Geotab MyAdmin API in three stages: 1) authentication, 2) provisioning, and 3) data transfer as follows.
- Authentication — Prove your identity as a legitimate and registered Geotab Reseller or Partner.
- Provisioning — Register the third-party device on the Geotab platform as a vehicle or device within a customer database (Done only once).
- Data Transfer — Submit data to the platform via the MyAdmin API, and retrieve from a database via the Geotab API.
Supported data types for third-party telematics devices
With all that technical information being said, it’s also important to mention that the types of telematics data that can be transferred to MyGeotab from third-party devices includes:
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Speed
- Date and time
- Ignition status (on/off)
- Auxiliary relay status for up to 8 relays
- Engine/Diagnostic data
- Device data
This field of datasets allows a huge variety of telematics devices to be integrated by Geotab Partners, Resellers, or vendors from many industries.
More resources on third-party device integration for Geotab
Are you looking to integrate with Geotab? Do you have a telematics device that you want to communicate with the Geotab cloud platform? For more technical information, look to our online Third-party device MyAdmin SDK document.
If you are a Geotab Partner or Reseller looking for next steps, read the document Third-Party Telematics Devices for MyGeotab.
The support for third-party devices with Geotab ushers in a whole new world of exciting possibilities for a variety of different devices to collect, share, search, and analyse rich telematics data. These devices can come from Geotab, or a varied variety of companies offering the unique benefits of each in one unified portal Through third-party device integration, companies can discover new ways to view their data, gain insight into their business processes, and solve critical business challenges.
Related:
Expand your telematics solution: Third-party device integration with IOX technology
How we protect your MyGeotab telematics data with backup and recovery
15 Security recommendations for building a telematics platform resilient to cyber threats
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
The Geotab Team write about company news.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to get industry tips and insights
Related posts

Field service is losing money to bad data: Go beyond GPS with smarter telematics
June 27, 2025
3 minute read


Enhancing winter road maintenance with postseason materials usage analyses
June 20, 2025
6 minute read

Building a self-sustaining school bus driver safety program with Geotab Vitality
June 13, 2025
7 minute read

The impact of unproductive idling on police vehicle service life
June 10, 2025
3 minute read

Unlock field service ROI: Your practical guide to connected operations playbook
June 9, 2025
3 minute read